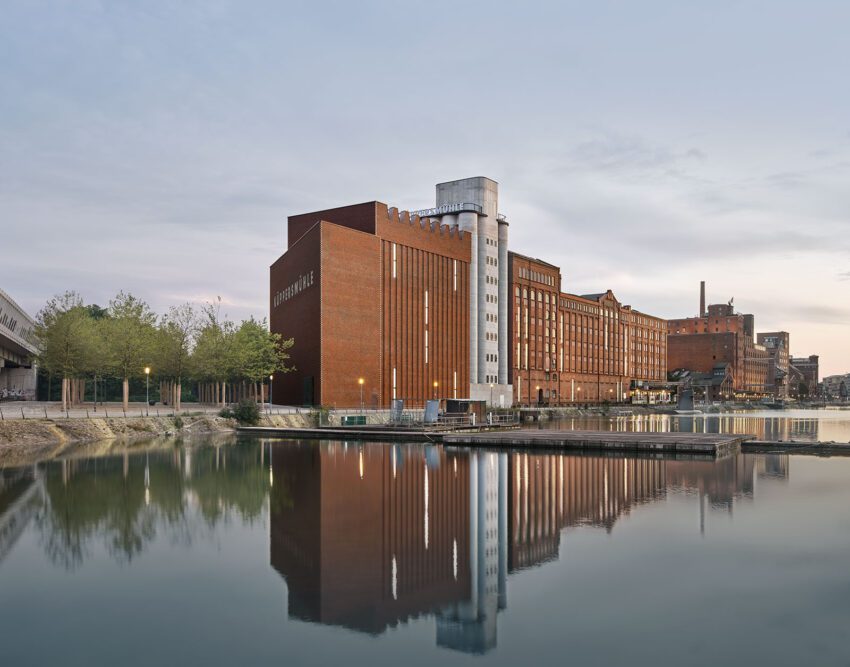
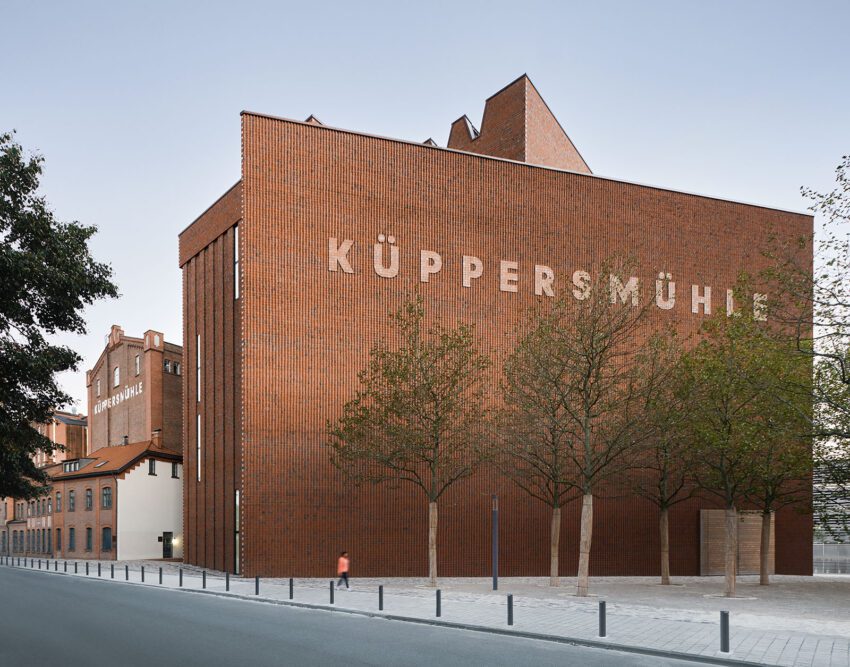
Situated in Duisburg’s Inner Harbour, the Museum Küppersmühle (MKM) is a testament to the architectural prowess of Herzog & de Meuron. Originally a grain mill built in 1860, the structure was transformed into an art museum in 1999, housing the Ströher Collection, one of the most comprehensive private collections of German post-war art. Showcasing works by renowned artists such as Georg Baselitz, Gerhard Richter, and Rosemarie Trockel, the museum has been expanded to accommodate its ever-growing collection. The extension project, initiated in 2013, blends seamlessly with the historic brick buildings along the dockside, creating a harmonious ensemble. The new structure, consisting of three parts and providing additional exhibition space, is designed to make optimal use of the available area while respecting the existing architecture. With this revitalization, the Museum Küppersmühle continues to celebrate the rich artistic heritage of Germany.
MKM Museum Technical Information
- Architects1-2: Herzog & de Meuron
- Location: Duisburg, Germany
- Client: MKM Stiftung, Berliner Allee 65, Darmstadt, DE
- Topics: Museums
- Gross Floor Area: 5,000 m2 | 53,819 ft2
- Project Year: 2013 – 2021
- Photographs: © Simon Menges
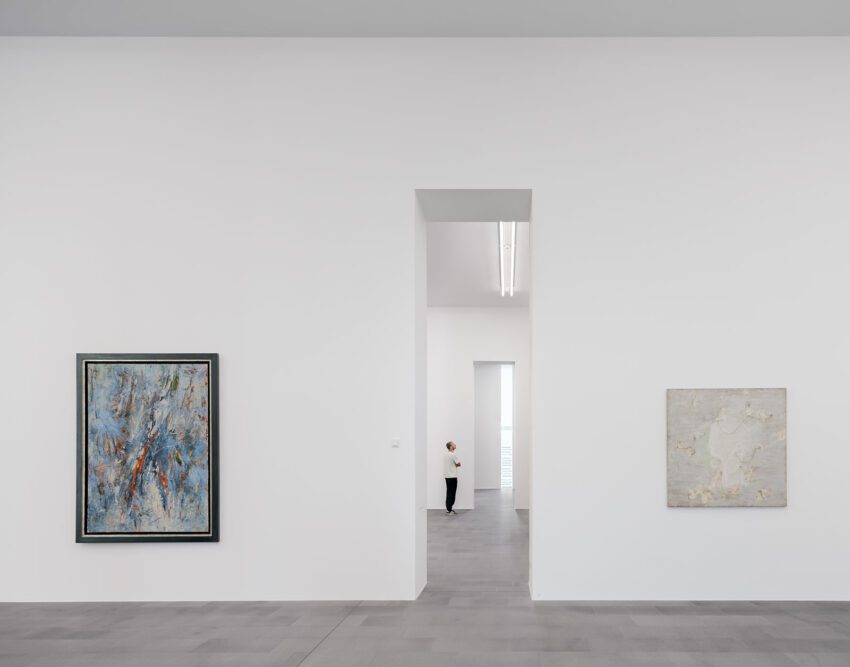
The MKM Museum Küppersmühle presents key works and groups of works from the Ströher Collection, one of the most extensive private collections of German post-war art – to date on 2,500 m2 of exhibition space. With over 2,000 works, the collection comprises central positions of art development in Germany, from the immediate postwar period to the present.
– Herzog & de Meuron Architects
MKM Museum Photographs
Text by the Architects
Küppersmühle
A grain mill was erected in 1860 on the site of the present Museum Küppersmühle by industrialist Wilhelm Vedder, one of the founding fathers of Duisburg’s Inner Harbour. In 1900 the first mill using the most up-to-date technology went into operation in the Inner Harbour, which became known as the ‘bread basket of the Ruhr district,’ and in 1908, the earlier buildings were replaced by the three-part structure now housing the museum. The business was taken over in 1912 by the Werner & Nicola Works, who added a boiler house with a chimney. The adjoining steel silos were constructed in the 1930s. In 1969 the company merged with the Küppers works of Homberg, which gave its name to the mill and the museum. The mill closed down in 1972.
The Museum Küppersmühle (MKM), a project by Herzog & de Meuron dating from 1999, was the first milestone in transforming the Inner Harbour into an attractive focus of urban life. As a museum, the former mill, with its historic brick elevations, became the center of a new, high-grade, multi-use inner-city location. Since 1999 the Küppersmühle has housed an art museum, run by the Stiftung für Kunst und Kultur e.V. (a registered cultural association in Bonn), that contains one of the finest collections of German art from the 1950s to the present.
The Ströher Collection
The MKM Museum Küppersmühle presents key works and groups of works from the Ströher Collection, one of the most extensive private collections of German post-war art – to date on 2,500 m2 of exhibition space. With over 2,000 works, the collection comprises central positions of art development in Germany from the immediate postwar period to the present. The focus is on painting, but the collection also includes sculpture and photography.
Over time, a desire for a building capable of housing all the works of art and displaying them in a manner worthy of a collection that includes many artists whose major significance is recognized internationally, among them Georg Baselitz, K. O. Götz, Jörg Immendorff, Anselm Kiefer, Sigmar Polke, Gerhard
Richter, Fred Thieler and Rosemarie Trockel.
Extension project
An extension to accommodate the collection was to be erected in 2008 on top of the silo towers. Faulty work by the steel-working company involved and the company’s subsequent insolvency meant that the steel-frame construction could not be installed. Construction work ceased, and the project was abandoned owing to financing problems encountered by the client, the real estate company GEBAG. The building complex became the property of the Ströhers.
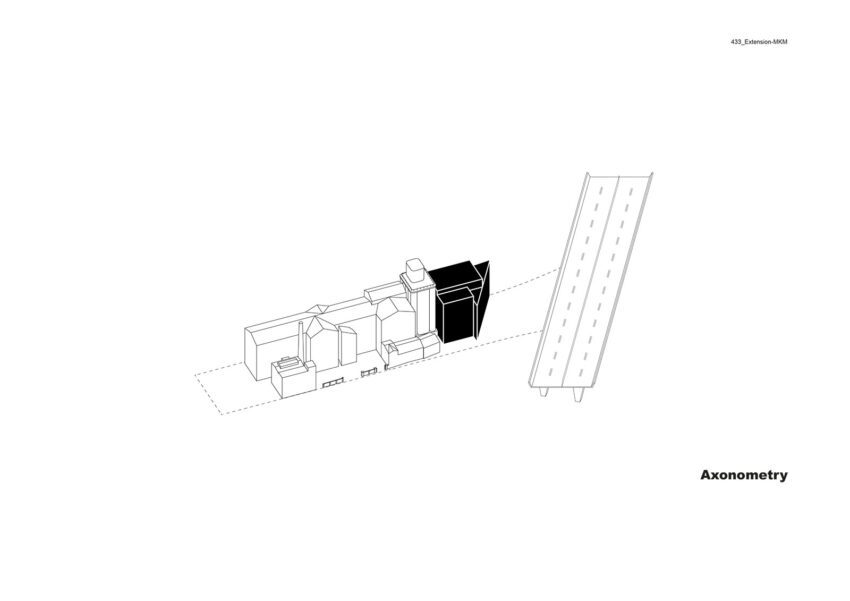
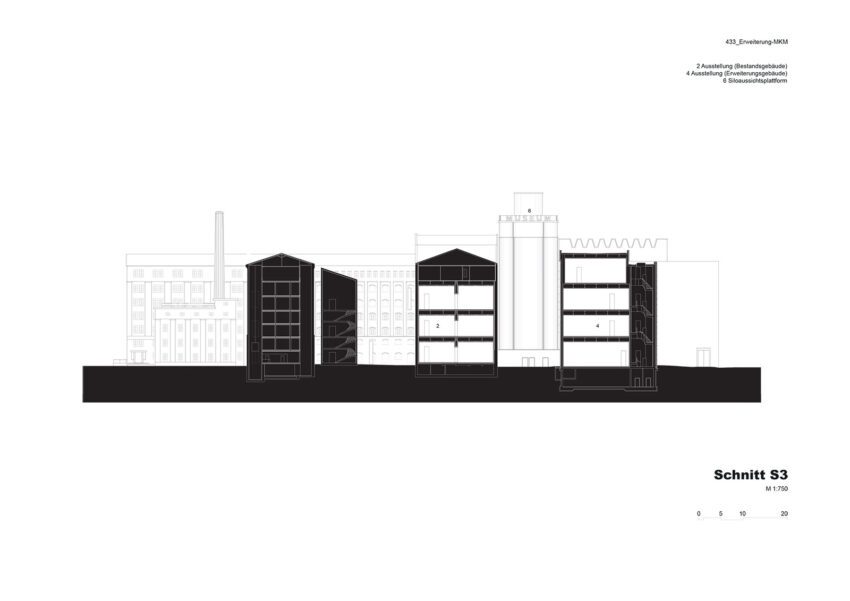
The extension project was activated in 2013, with the Ströher family as clients. A feasibility study undertaken by Herzog & de Meuron explored the site’s potential under current conditions. The resulting project constitutes a radical new start. The original idea of an illuminated cube balanced on the silo towers and visible from afar has been scrapped. Instead, we propose to erect a building whose dimensions and materials accord with the sequence of historic brick structures lining the dockside. The new structure thus completes the existing museum complex in a visually appropriate way and forms a suitable conclusion to the row of buildings along the dock. At first glance, it might seem like the new building had always been there.
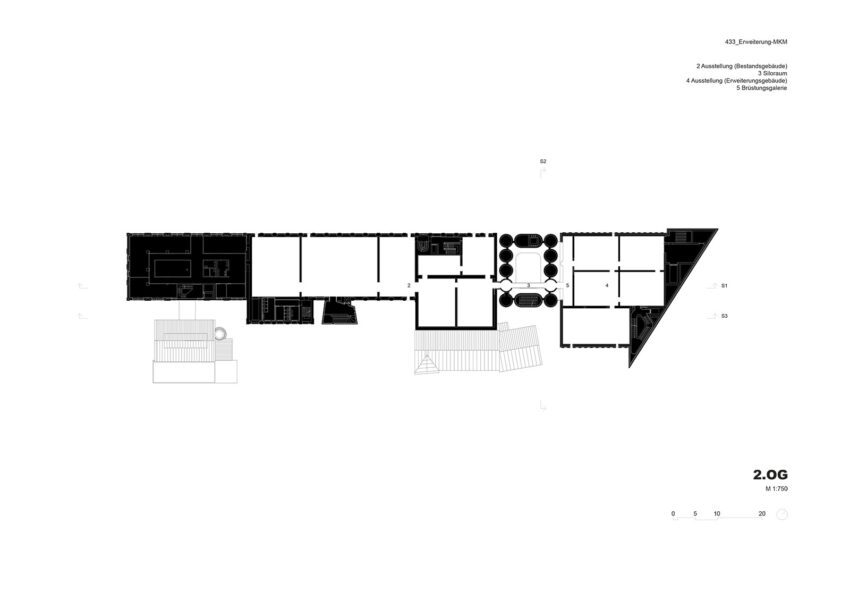
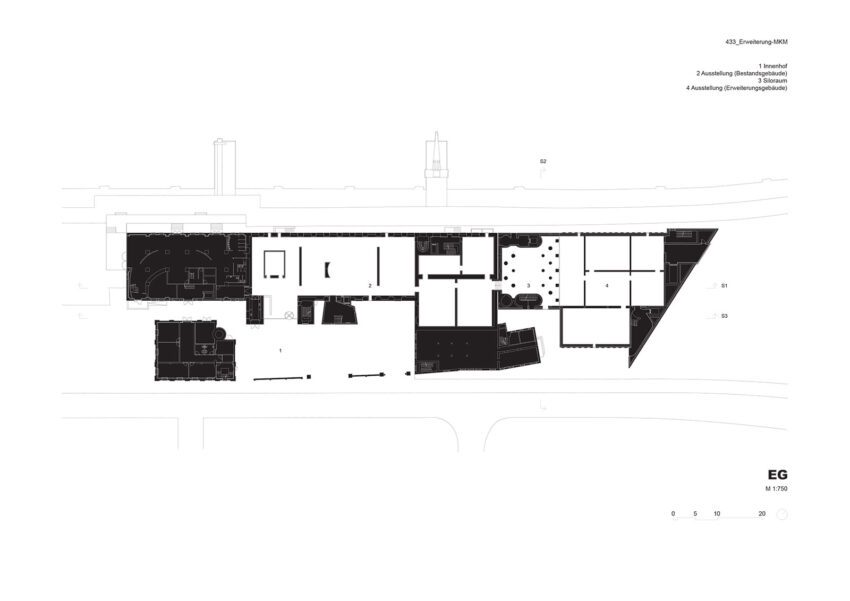
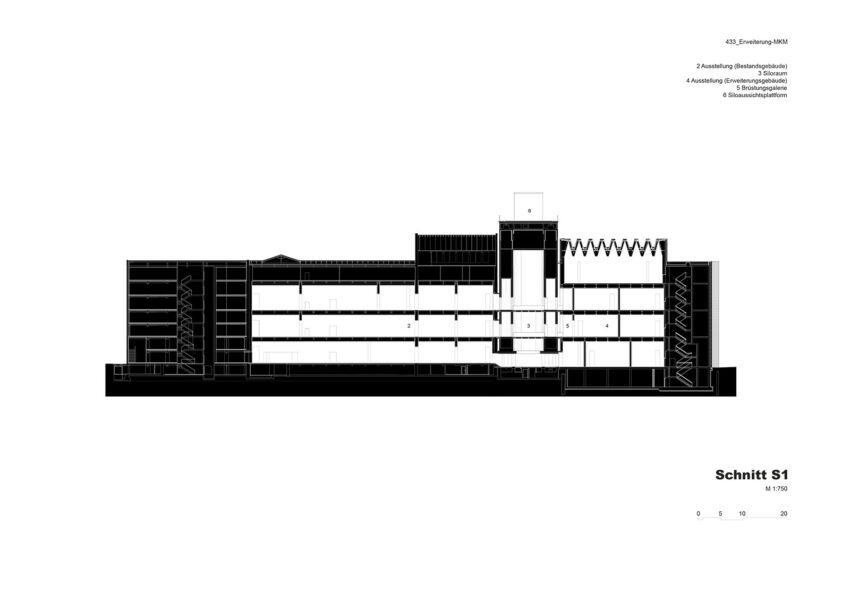
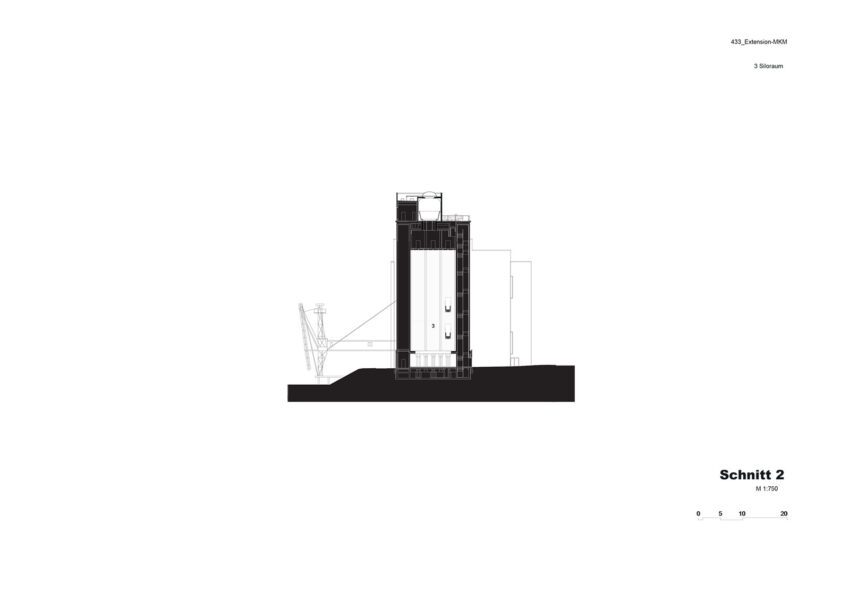
The new structure consists of three parts with a height of approximately 33.5, 30.5, and 27.5 meters, respectively. In terms of mass, height, and materials, they take their cue from the existing buildings, continuing them and rounding them off to form a harmonious whole. Two parts contain the exhibition areas; the third provides access and houses utilities and art handling facilities. With five levels, one below-ground floor space amounts to some 4,900 square meters and exhibition areas of roughly 2,500 square meters.
Massing was crucially influenced by a ban on buildings within forty meters of the autobahn. Optimum use is made of the available area. The arrangement of the exhibition structures – the tallest of the three parts and the smaller one adjoining it – echoes the course of the building-free zone, while one elevation of the third part runs along its boundary. The additively composed parts remain distinctly legible. At its tallest point (the uppermost level of the larger exhibition component), the new structure is related in height to the main existing building.
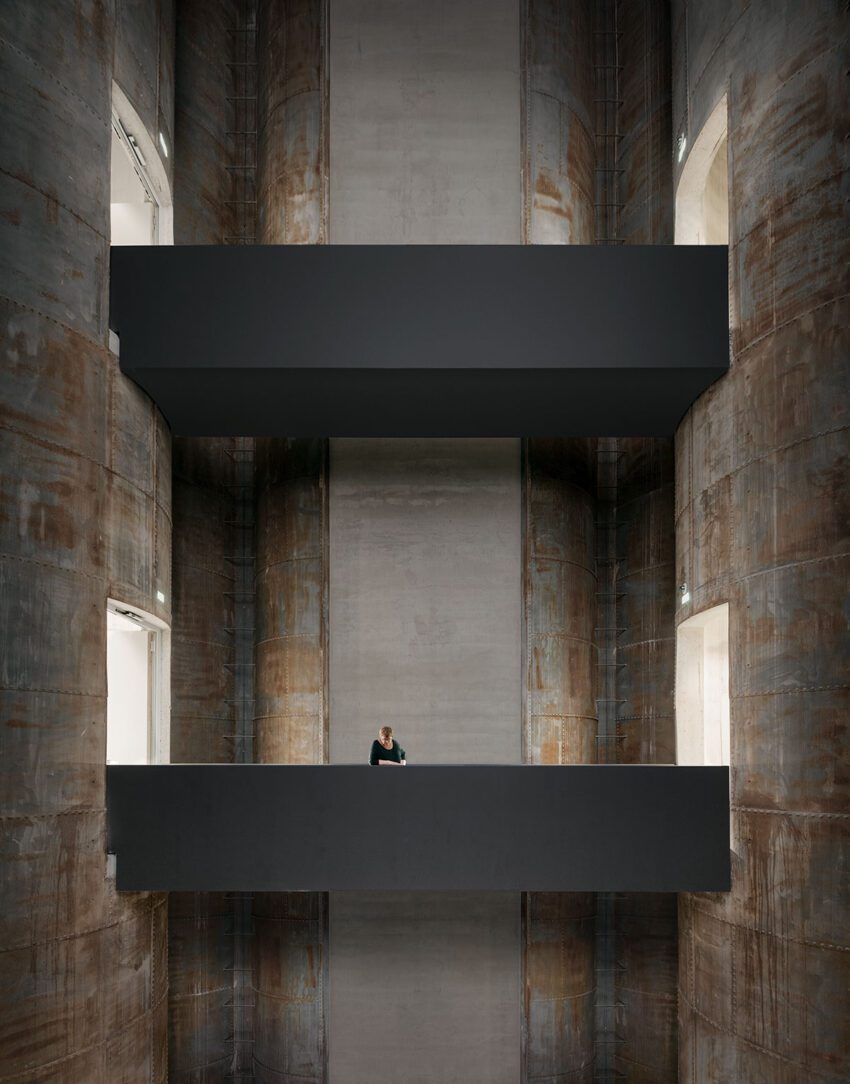
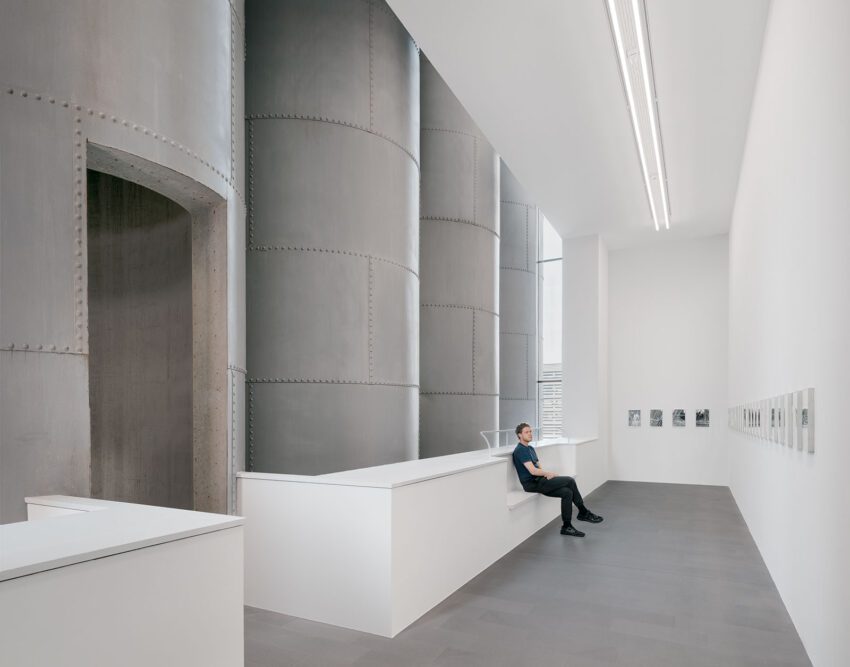
The extension is to be linked directly to the existing exhibition spaces by bridges through the silos at the first and second upper levels, facilitating uninterrupted visitor access throughout the museum. Similarly, the height of the new exhibition areas takes its cue from the existing galleries. The silos will not only be converted into elements connecting the old with the new but also house distinctive exhibition spaces. However, their original materials are to be retained because the silos are an indispensable ‘sculptural’ component of the Küppersmühle as an industrial monument. Long reduced to this historical and aesthetic aspect, they acquire a new function through refurbishment as access links and display areas. Six internal silos had already been removed. Now, with the ground-floor ceiling opened up and the insertion of the bridges, the entire space will be visible to visitors. In addition, the silos can be seen from some of the exhibition areas.
As in the existing galleries, windows in the elevations facing the dock and Philosophenweg offer varied and striking views of the site and its surroundings. The material of the elevations echoes the brick of the existing buildings.
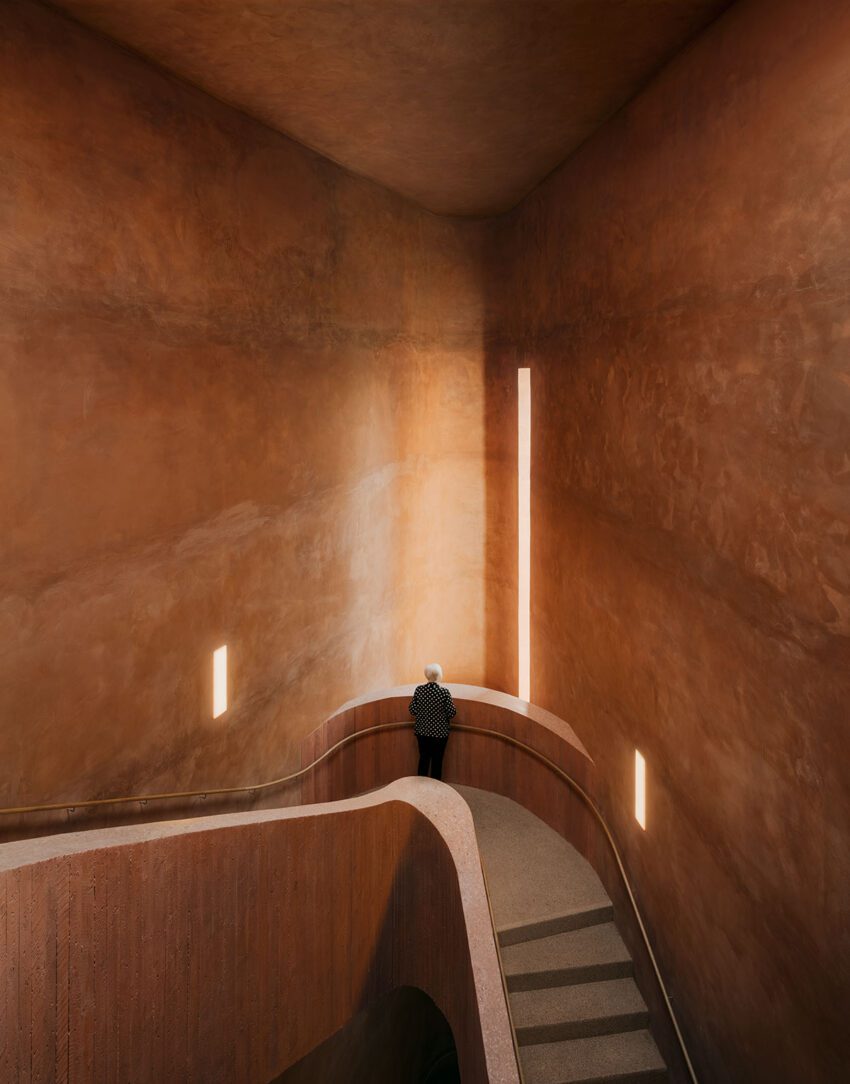
A staircase permits continuous visitor circulation and the arrangement of all the exhibits in a consecutive
sequence. In conception and spatial context, the staircase is related to that featured in the museum project of 1999.
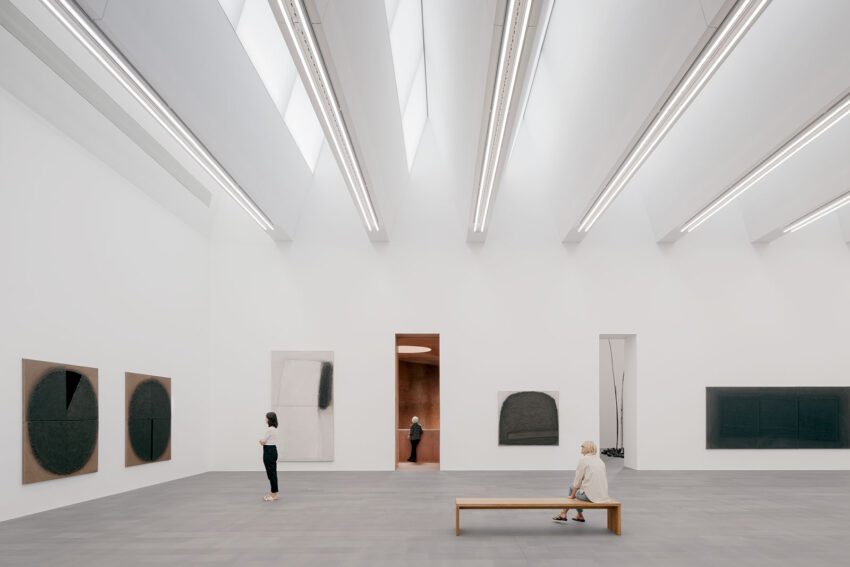
The new exhibition areas echo the overall additive character of the Küppersmühle as a typical industrial facility of the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. The galleries echo the existing exhibition spaces in their architecture and interior design. The uppermost display area, which is not directly accessible from the existing building, consists of a visible shed construction with top lighting. All exhibition levels have a spatial arrangement facilitating multiple flexible uses.
The silos are to be fitted out with a superstructure, as they were originally in the 1930s. Featuring a viewing platform accessible from the dockside promenade, the superstructure will grant the silos yet another new function.
MKM Museum Plans
MKM Museum Image Gallery













About Herzog & de Meuron
Herzog & de Meuron is an internationally renowned architecture firm based in Basel, Switzerland. The firm was founded in 1978 by Jacques Herzog and Pierre de Meuron, both Swiss architects. The duo has gained recognition for their innovative and distinctive designs, often merging traditional materials with contemporary aesthetics. They have been involved in numerous high-profile projects, such as the Tate Modern in London, the Bird’s Nest Stadium in Beijing, and the Elbphilharmonie in Hamburg. In 2001, Herzog & de Meuron were awarded the Pritzker Architecture Prize, one of the most prestigious awards in the field of architecture.
Works from Herzog & de Meuron
- Partners: Jacques Herzog, Pierre de Meuron, Robert Hösl (Partner in Charge)
- Project Team: Roland Schreiber (Project Architect/ Project Manager), Mikolaj Bazaczek, Juliane Brantner, Teodor-Octavian Cuciureanu, Florian Hartmann, Sebastian Hefti, Māra Igaune, Susanne Kozlowski, Hannah Reusser, Daniel Schürer
- General Planning: Drees & Sommer Schweiz GmbH
- HVAC Engineering: Drees & Sommer Advanced Building Systems
- Structural Engineering: Drees & Sommer Advanced Building Systems
- Construction Management: Diete + Siepmann Ingenieur GmbH
- Landscape Architect: Vogt Landschaftsarchitekten
- Fire Protection Consulting: HHP Berlin